The ENES Data Space delivers an open, scalable and cloud-enabled data science environment for climate data analysis on top of the EOSC Compute Platform. It provides both storage and computational capabilities.
It consists of a JupyterLab instance jointly with a large set of pre-installed Python libraries and a ready-to-use Ophidia HPDA framework instance for running data manipulation, analysis and visualization.
The ENES Data Space hosts (open) data from the ESGF federated data archive on compute cloud to support researchers in realistic climate model analysis experiments.
Data pool and tools
The ENES Data Space provides access to a set of specific CMIP variable-centric collections. Data are
downloaded and kept in sync with the ESGF federated data archive within a disk space of about 150 TB.
In particular, about 30TB of CMIP6 data for multiple models, scenarios (e.g., historical, ssp245,
ssp370 and ssp585) and variables (air temperature, precipitation, near-surface wind, specific and
relative humidity) with different temporal resolutions (yearly, monthly, daily, 6-hourly) are immediately available for the users.
A JupyterLab environment is equipped with a set of ready-to-use Python modules for data management,
analytics and visualization to support users data analysis.
You can exploit the
intake-esm data cataloging utility for searching and discovery of the available CMIP6 datasets
and loading assets into xarray datasets as well as into the Ophidia workspace.
Login here to access and exploit the
JupyterLab environment.


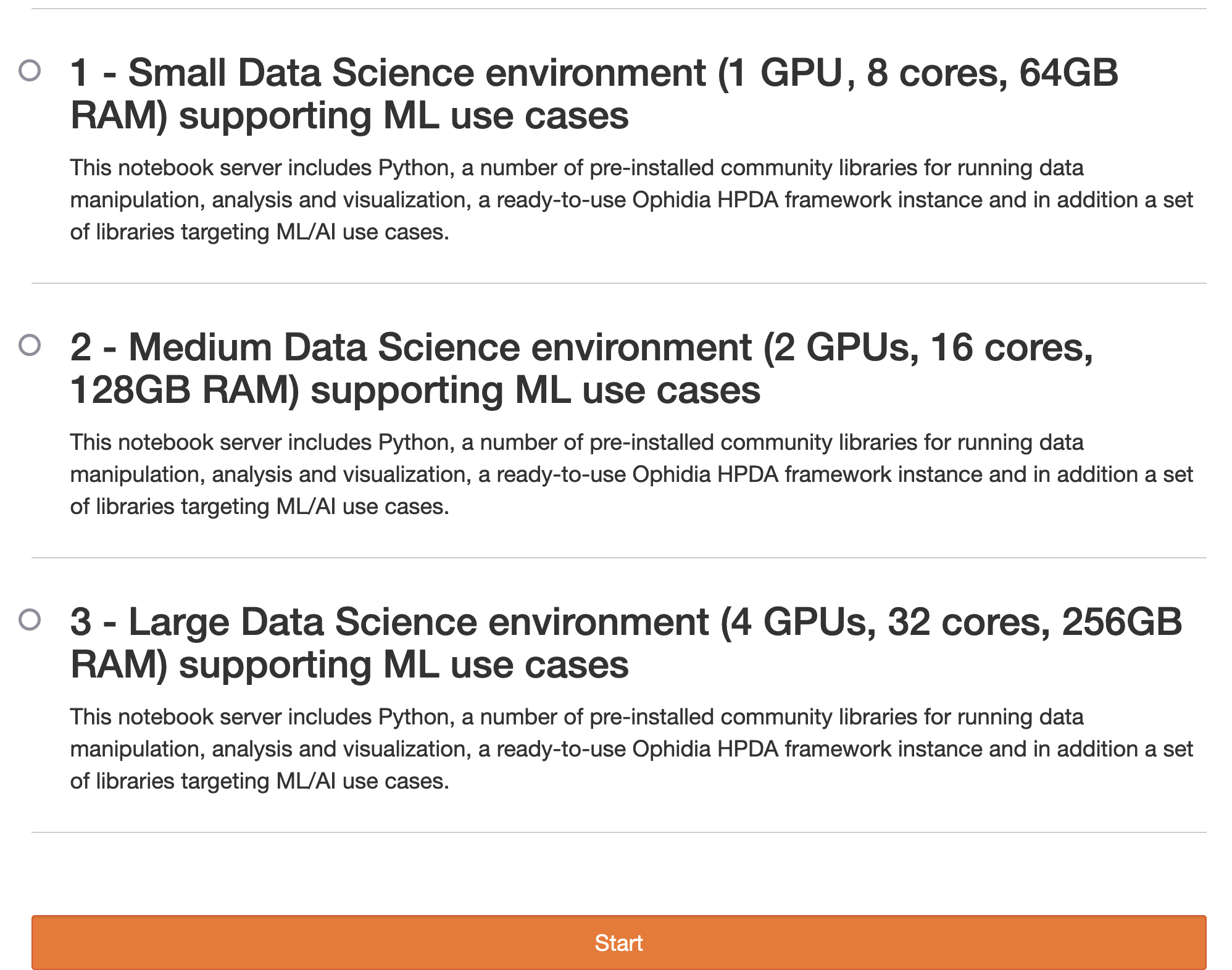
Computational profiles
The ENES Data Space environment targets a wide range of use cases from the climate and weather domains: computation of climate indices, machine learning training and inference, big data processing, interactive analytics, data visualization, etc.
To this end, different computational profiles are available to support the most frequent scenarios requested by scientists. New profiles can be added as well to cater to new user requirements and application workloads.
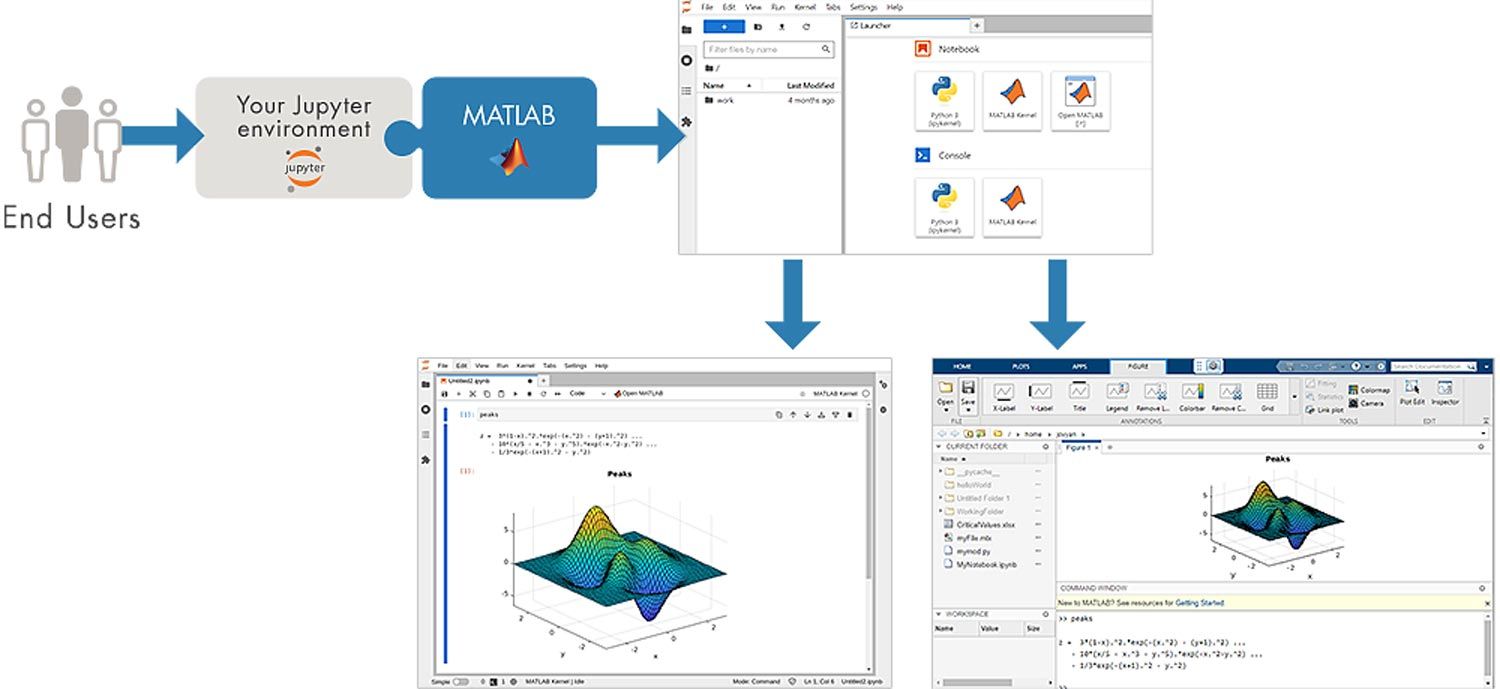
The ENES Data Space environment also provides support to use cases implemented in MATLAB.
MATLAB Integration
Geo- and climate scientists around the globe use MATLAB to analyze, process and visualize climate data. Now, users of the ENES Data Space can login and start using MATLAB directly within the Jupyter-based environment, thus exploiting its powerful features to access and analyze data on the cloud. Users can either use the familiar MATLAB environment in a browser or the MATLAB kernel – available via the MATLAB Integration for Jupyter. An example to get started is available here.